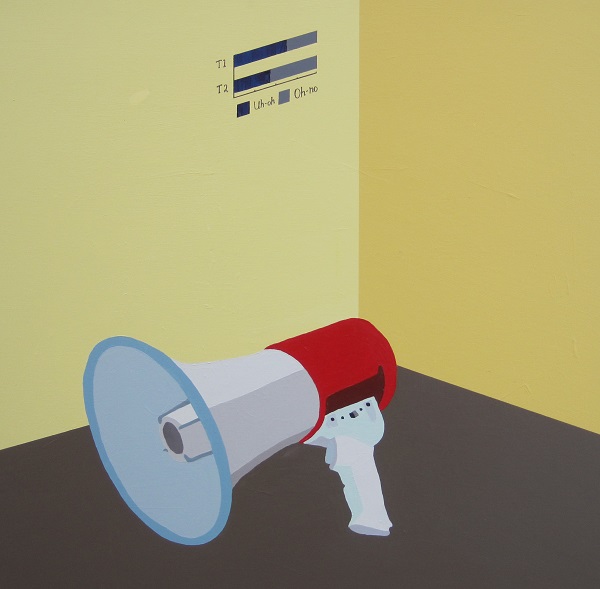


What is a corner? The corner represents a symbolic value. Children are told to stand in the corner when they are disobedient. The corner is a place where one meditates on one’s shortcomings. One can be ‘backed into a corner’ and left with few options or one can retreat into a corner for safety. Animals corner their prey. Corners are places where things get lost and are found. Corners are neglected and swept in the spring. Unfortunate artists can paint themselves into a corner if they are not aware of the space around them and the area beneath their feet. Corners are forgotten with the bustle of activity in the centre of the room.
Gilles Deleuze’s book on Francis Bacon contains a short chapter in which he describes some of the possible reasons for why Bacon consistently displayed his figures against a “round area or ring.”1 Deleuze asserts that the main reason for utilizing this “simple technique” is to create a “place” and to isolate the Figure.2 There is a progression and fatefulness in assigning the Figure to this place. Deleuze claims that the round area or ring relates the Figure to the setting and, in so doing, posits the Figure or painting as a kind of fact or isolated reality.3
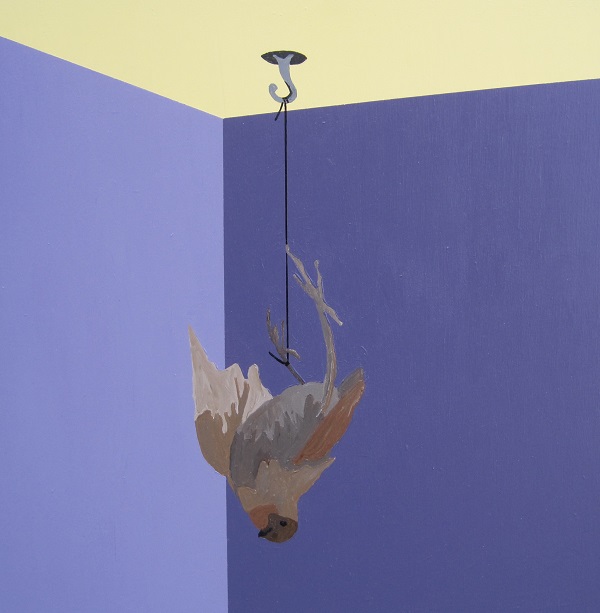

The horizon, ring, corner or wall is a painterly convention frequently revisited by contemporary artists. Although many painters have excluded these settings in favour of fields (e.g. a field of pure colour, or a field of refuse), such settings are useful constructs for displaying objects of value or inducing value within objects. Fields are distinct from settings in that they form a systematic or total (rather than operative or local) context for objects. Conversely, settings function by separating the object from its context so that the viewer can have an unmediated experience of that object. The setting recedes ‘into the background’ as a decorative relief or incidental support.
 Corners are specific settings that feature the intersection of three planes (i.e. two walls and a floor). The intersection forms a point. The corner can function simply as the intersection of three planes or as a construct that creates depth and dimensionality. This bivalent nature hints at its duplicity as a setting. It creates a false depth. In this respect, the play of surfaces conspires to become a point of convergence or vanishing point. As a convergence of three surfaces it is a point of ‘agreement’, or perhaps a type of foreclosure; three colours and three lines converge to form a dimensional whole. The duplicity of the corner consists of its character as both a play of surfaces and as a convergence of three lines. The duplicity consists in the fact that the corner realizes both the idea of form and the Form itself through both a convergence (of surface and line) and a construction (of dimensionality).
Corners are specific settings that feature the intersection of three planes (i.e. two walls and a floor). The intersection forms a point. The corner can function simply as the intersection of three planes or as a construct that creates depth and dimensionality. This bivalent nature hints at its duplicity as a setting. It creates a false depth. In this respect, the play of surfaces conspires to become a point of convergence or vanishing point. As a convergence of three surfaces it is a point of ‘agreement’, or perhaps a type of foreclosure; three colours and three lines converge to form a dimensional whole. The duplicity of the corner consists of its character as both a play of surfaces and as a convergence of three lines. The duplicity consists in the fact that the corner realizes both the idea of form and the Form itself through both a convergence (of surface and line) and a construction (of dimensionality).
Two of the most significant questions a painter may ask is, “What must I paint?” and “What is the painting about?” The idea of form contained in a painting is inevitably ‘about’ a sensation or perception. The painter’s nervous system is trained not only to recognize particular sensations and perceptions but to actualize them in the materiality of paint.4 Painters practice their art as a way of learning to live with a given set of perceptions and sensations. The act of representation in painting is therefore second to the sensations and perceptions which inaugurate it.
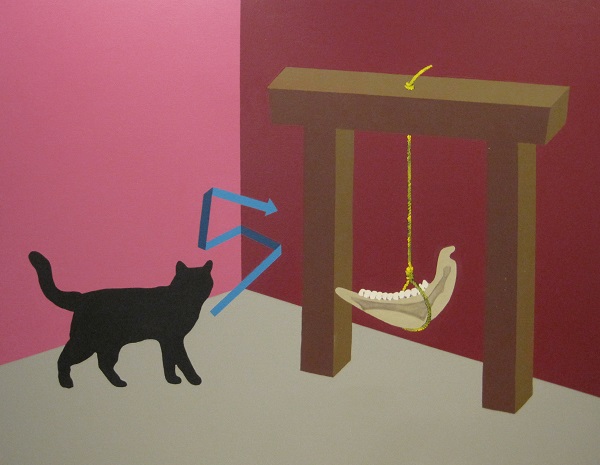

The critic’s judgment (i.e. the critique) is the genesis of painterly sensations and perceptions. Critique is the limit of art and limits art to what it alone can do. It functions as a form of violence that is inflicted, observed or endured and occurs when one form overcomes another or when a form is ‘deformed’ by a superior consciousness. The deformation heralds a new and hitherto unappreciated beauty. It is the beauty of a projection or displacement of the painter’s subjective point of view into the materiality of paint. The transformation of sensations and perceptions through the pure and practical reason of the painter reflects the painter’s critique of power. What power? The power of judgment. The critique is therefore absorbed into the very colour of the picture.
Ludwig Wittgenstein’s picture theory holds great explanatory appeal in these cases because it contains propositions regarding the logic and structure of a picture. The painter labels the painting with a title because it represents a state of affairs. There is a close correspondence between the fact represented by the title and the pictorial content of the painting. It is in this sense that the picture functions as a relation between the physical or material world and the thoughts of the painter. Within this context, pictures are criticological constructs. Their titles are statements or propositions that are endowed with sense. As a function of these statements the painting’s pictorial components correspond almost identically with a set of defined elementary forces.
The corner can therefore play several conscious roles within a painting. They are the place of an encounter between a convergence and a defined space. These corners embody a perception. Moreover, corners function as a limit. As the limit of pictorial space they set up a picture plane that functions as a limit to logical thought. By using corners in this way, painters can represent unusual objects with a degree of normative ‘factuality’ – even if they are only representations. Finally, corners function as a place or setting. These corners are settings in which something can take place as well as a destination for various ideas. They instantiate and materialize Form in unanticipated ways. For the Silo, Timothy deVries http://www.timothydevries.ca/
- Gilles Deleuze, Francis Bacon: The Logic of Sensation (New York: Continuum, 2003), 1
- Deleuze, Francis Bacon, 2
- Deleuze, Francis Bacon, 2
- Deleuze, Francis Bacon, 52


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.