Only 10% of rare diseases have an FDA-approved therapy. This sobering statistic highlights why research is so imperative for patients with rare diseases. Clinical trials can be a crucial opportunity to access life-saving treatments.
However, African-American, African-Canadian and Latino patients with rare diseases face significant underrepresentation in clinical trials. This lack of representation results in drugs being developed that aren’t proven safe or effective across different populations.
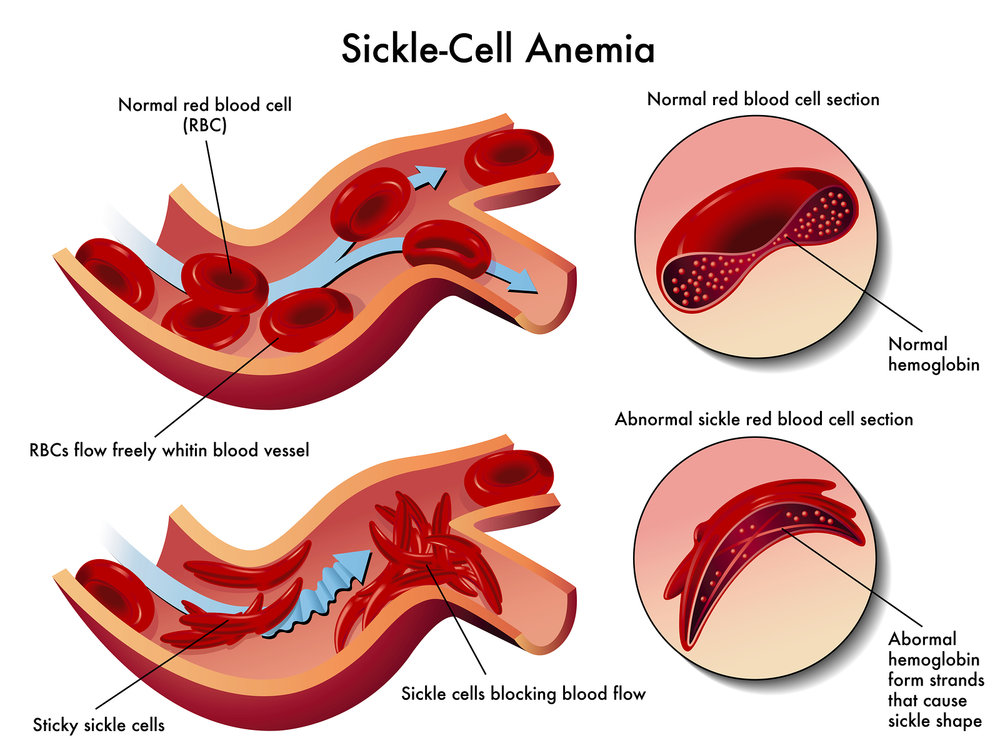
A 2018 research carried out by the U.S. Census Bureau stated that out of the 12% Black or African American population across the U.S., only 2.2% had participated in clinical trials for rare diseases. Sickle cell disease is one rare disease that predominantly affects the African American community.
India has close to 50-100 million people affected by rare diseases or disorders, with almost 80% of these rare condition patients being children. As per the U.S. Census Bureau, Indian Americans constitute 1.2% of the U.S. population, which translates to 4.5 million, as of 2021, and out of the 5.8% total Asian population across the U.S., their clinical trials participation in 2018 was only 1%.
When certain groups are underrepresented, the universal right to health is jeopardized, and the economic burden of public health care rises. Inequities in clinical research participation impede applications in drug efficacy, toxicity, therapeutic indices, and other areas. Furthermore, it has the potential to raise healthcare costs.
February is “Rare Disease Month”, while February 28th is “Rare Disease Day”, and 2023 is the 40th anniversary of “The Orphan Drug Act”—a law that was passed in the United States in 1983 to facilitate the development of orphan drugs—drugs for rare diseases.
Dr. Rajasimha, Founder and Executive Chairman of IndoUSrare says, “Rare Disease Month allows the rare disease community to come together and make themselves heard.”
The future of rare disease research and treatment still requires enhanced detection techniques, dissemination of understanding concerning optimal care, and research to prevent, treat, and cure disease, and IndoUSrare collaborates with researchers in the U.S. and other western countries with their counterparts in the Indian subcontinent to engage and include the large and diverse populations of Indians in India and globally.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.