Arguments and questions keep rising following the FAA outage that happened early this year on January 11th, 2023, which resulted in the complete closure of the U.S. Airspace and most of the airspace here in Canada.

Although the FAA later confirmed that the outage was, in fact, caused by a contractor who unintentionally damaged a data file related to the Notices to Air Missions (NOTAM) system, the authenticity of the fact is still debated.
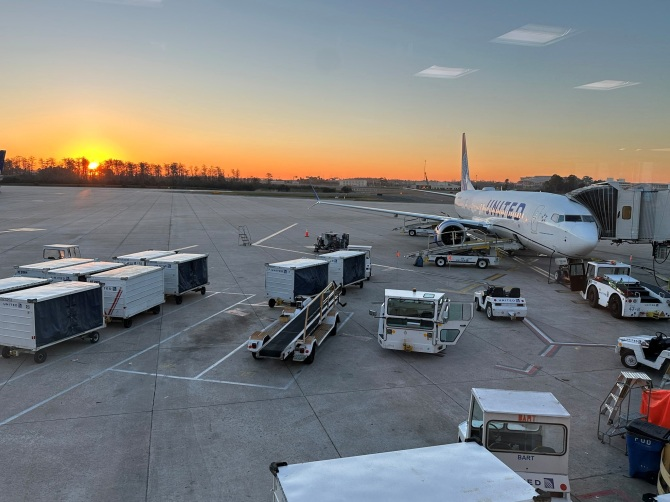

The FAA initially urged airlines to ground domestic departures following the system glitch Credit: Reuters
“The FAA said it was due to one corrupted file – who believes this? Are there no safeguards against one file being corrupted, bringing everything down? Billions of Dollars are being spent on cybersecurity, yet this is going on – are there any other files that could be corrupted?” questions Walt Szablowski, Founder and Executive Chairman of Eracent, a company that specializes in providing IT and cybersecurity solutions to large organizations such as the USPS, Visa, U.S. Airforce, British Ministry of Defense — and dozens of Fortune 500 companies.
There has been a string of cybersecurity breaches across some high-profile organizations recently. On January 19th, T-Mobile disclosed that a cyberattacker stole personal data pertaining to 37 million customers, December 2022 saw a trove of data on over 200 million Twitter users circulated among hackers. In November 2022, a hacker posted a dataset to BreachForums containing up-to-date personal information of 487 million WhatsApp users from 84 countries.
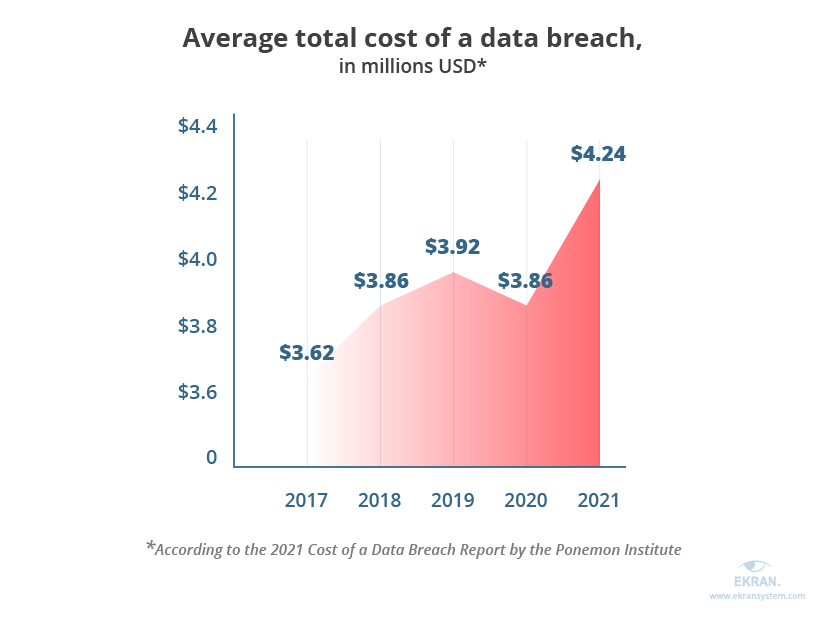
The Ponemon Institute in its 2021 Cost of a Data Breach Report analyzed data from 537 organizations around the world that had suffered a data breach. They found that healthcare ($9.23 million), financial ($5.72 million), pharmaceutical ($5.04 million), technology ($4.88 million), and energy organizations ($4.65 million) suffered the costliest data breaches.
The average total cost of a data breach was estimated to be $3.86 million in 2020, while it increased to $4.24 million in 2021.
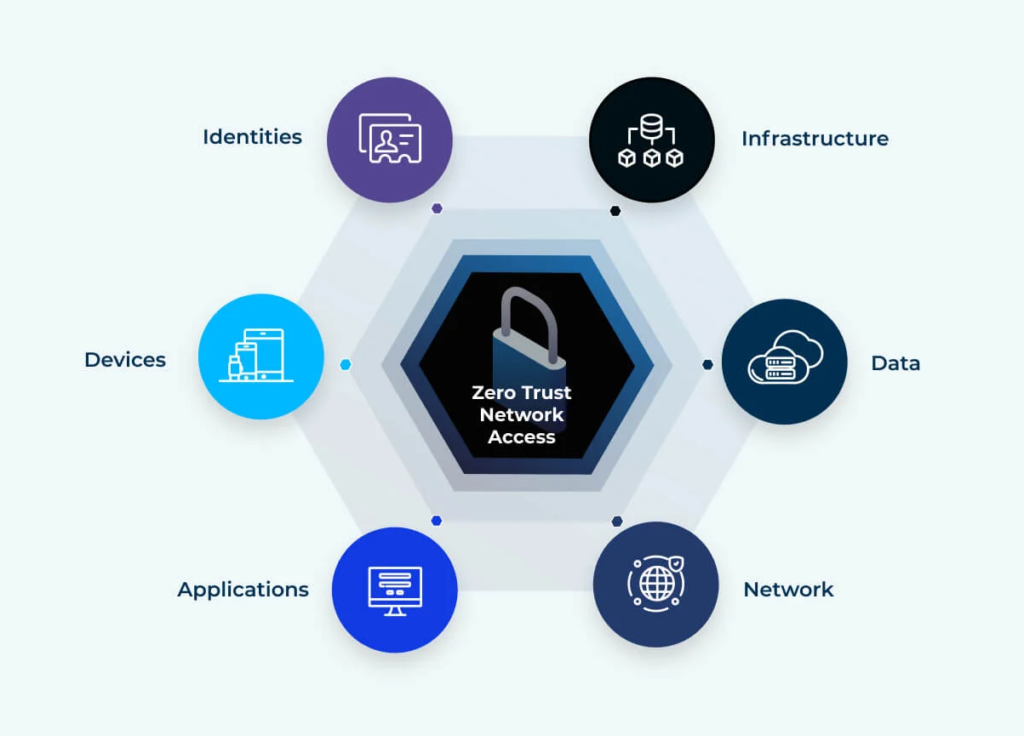
“In the software business, 90% of the money is thrown away on software that doesn’t work as intended or as promised,” argues Szablowski. “Due to the uncontrollable waves of costly network and data breaches, the U.S. Federal Government is mandating the implementation of the Zero Trust Architecture.“

Eracent’s ClearArmor Zero Trust Resource Planning (ZTRP) consolidates and transforms the concept of Zero Trust Architecture into a complete implementation within an organization.

“Relying on the latest technology will not work if organizations do not evolve their thinking. Tools and technology alone are not the answer. Organizations must design a cybersecurity system that fits and supports each organization’s unique requirements,” concludes Szablowski. For the Silo, Karla Jo Helms.

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.